Proxie 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome
Proxie is a HTTP debugging proxy for macOS. It puts a proxy between HTTP clients and the Internet. After a proper configuration of proxy settings, all HTTP traffic will go through Proxie and be available for inspection. Any Platform - Proxie records all HTTP traffic from any. The basic syntax of the Proxy-Authenticate header is as follows: Proxy-Authenticate: realm=. The value can be any of the handful of valid authentication schemes allowed in HTTP/1.1, with the most common authentication scheme being Basic, which accepts a username and password credential pair to validate authentication.
- Proxy 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome Settings
- Proxy 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome Extension
- Proxy 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome Browser
- Proxy 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome Default
Getting proxy server not responding google chrome Error even if your modem, router, and all other WiFi devices are ok. This is a common error in Chrome, Internet Explorer and other browsers for the user’s Windows 10, 8.1 and 7. The unable to connect to the proxy server error in Windows 8 or Windows 10 can be caused by several reasons like installing a third party proxy program that might malfunction or perhaps your antivirus blocks your access to the proxy server. This happens mostly when a malicious adware or proxy program messes up with your computer proxy settings.
There are several reasons for this error, one basic cause is due to some unwanted application or a program. Or can be due to some malicious extension. Also, this error can occur due to the misconfiguration in the LAN Settings.
Post Contents :-
- 1 Proxy server not responding
Proxy server not responding
If you are also suffering from this error and looking for a solution to fix this problem permanently. Here follow bellow tips to fix this error. First, we recommend to Install a good antivirus or anti-malware program with the latest update And perform a full system scan. Because mostly whenever you visit a website having malicious links and adware, they install themselves on the computer and change proxy settings without user content. So don’t forget to scan your computer using an antivirus or antimalware application. Now after scanning process complete Restart the windows and check the problem solved. If you still getting the same error then the cause may be different fallow next step.
Manually Resetting the Proxy Settings
Some time due to virus infection or any other Reason the proxy may get changed, it’s better to check and manually reset the proxy setting.
- To do this Go to Control Panel
- Click Internet Option then move to the Connections tab
- here Click on LAN settings button.
- Uncheck the box to “Use a proxy server for your LAN“
- And also make sure Automatically detect setting box is checked.
- Now click ok to save changes.
Again Once Restart the system and check problem got solved or not. Most of the time this step fix the problem but if for you the problem not solved then fallow the next step.
Reset Google Chrome to default
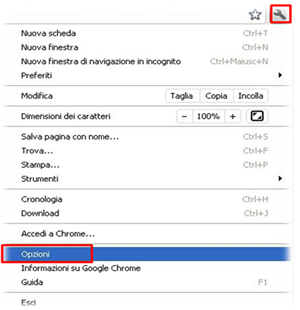
- Click on Chrome’s main menu button, represented by three horizontal lines.
- When the drop-down menu appears, select the option labeled Settings.
- Chrome’s Settings should now be displayed in a new tab or window, depending on your configuration.
- Next, scroll to the bottom of the page and click on the Show advanced settings.
- Scroll down to the Reset browser settings section is visible.
- Next, click on the Reset browser settings button.
- A confirmation dialog should now be displayed, detailing the components that will be restored to their default state should you continue on with the reset process.
- To complete the restoration process, click on the Reset button.
Proxy 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome Settings
Reset Internet Explorer Settings
- Press Windows Key + R then type inetcpl.cpl and ok to open Internet Properties.
- In the Internet settings window switch to the Advanced tab.
- Click on the Reset button and internet explorer will start the reset process.
- In the next window that comes up make sure to select the option “Delete personal settings option.“
- Then click Reset and wait for the process to finish.
- Reboot the Windows 10 device again and check if you are able to Fix The proxy server isn’t responding error.
Proxy 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome Extension
Use Registry Tweak to Delete Proxy virus
- Press Windows Key + R then type regedit and hit Enter to open Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the following registry key:
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER Software Microsoft Windows Current Version Internet settings
- Now in the right window pane right-click on ProxyEnable DWORD and select Delete.
- Also delete the following keys ProxyServer, Migrate Proxy, and Proxy Override.
- That’s all now Restart windows to make changes effective. And Check your problem solved.
Proxy 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome Browser
Did these solutions help to fix proxy server not responding google chrome? Let us know on comments below, also read:
Proxy 2 4 1 – Http Debugging Proxy Google Chrome Default
For Developers > Design Documents > HTTP authentication
Subpages (1):Writing a SPNEGO Authenticator for Chrome on Android |