Startupizer 2 3 3 – Advanced Login Handler
- Startupizer 2 3 3 – Advanced Login Handlers
- Startupizer 2 3 3 – Advanced Login Handler Login
- Startupizer 2 3 3 – Advanced Login Handler Portal
A quick logging primer¶
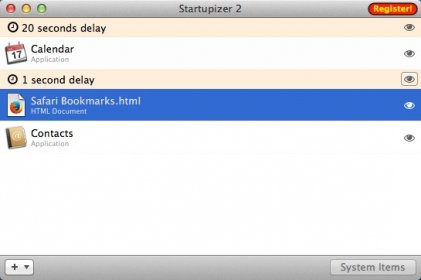
Startupizer is an advanced yet simple to use login items handler. It greatly enhances built in OS X login items functionality by offering conditional startup and dependencies management. This results in just the subset of applications and documents you need at a given time. centerbStartupizer v2.2.4 For MacOSX 4.83 Mb/b/center Startupizer 2 is advanced yet simple to use login items handler. It greatly enhances built in OS X login items functionality by offering conditional startup and dependencies management. This results in just the subset of applications and documents you need at a given time.
Django uses Python’s builtin logging module to perform system logging.The usage of this module is discussed in detail in Python’s own documentation.However, if you’ve never used Python’s logging framework (or even if you have),here’s a quick primer.
The cast of players¶
A Python logging configuration consists of four parts:
Loggers¶
A logger is the entry point into the logging system. Each logger isa named bucket to which messages can be written for processing.
A logger is configured to have a log level. This log level describesthe severity of the messages that the logger will handle. Pythondefines the following log levels:
DEBUG: Low level system information for debugging purposesINFO: General system informationWARNING: Information describing a minor problem that hasoccurred.ERROR: Information describing a major problem that hasoccurred.CRITICAL: Information describing a critical problem that hasoccurred.
Each message that is written to the logger is a Log Record. Each logrecord also has a log level indicating the severity of that specificmessage. A log record can also contain useful metadata that describesthe event that is being logged. This can include details such as astack trace or an error code.
When a message is given to the logger, the log level of the message iscompared to the log level of the logger. If the log level of themessage meets or exceeds the log level of the logger itself, themessage will undergo further processing. If it doesn’t, the messagewill be ignored.
Once a logger has determined that a message needs to be processed,it is passed to a Handler.
Handlers¶
The handler is the engine that determines what happens to each messagein a logger. It describes a particular logging behavior, such aswriting a message to the screen, to a file, or to a network socket.
Like loggers, handlers also have a log level. If the log level of alog record doesn’t meet or exceed the level of the handler, thehandler will ignore the message.
Startupizer 2 3 3 – Advanced Login Handlers
A logger can have multiple handlers, and each handler can have adifferent log level. In this way, it is possible to provide differentforms of notification depending on the importance of a message. Forexample, you could install one handler that forwards ERROR andCRITICAL messages to a paging service, while a second handlerlogs all messages (including ERROR and CRITICAL messages) to afile for later analysis.
Filters¶
A filter is used to provide additional control over which log recordsare passed from logger to handler.
By default, any log message that meets log level requirements will behandled. However, by installing a filter, you can place additionalcriteria on the logging process. For example, you could install afilter that only allows ERROR messages from a particular source tobe emitted.
Startupizer 2 3 3 – Advanced Login Handler Login
Filters can also be used to modify the logging record prior to beingemitted. For example, you could write a filter that downgradesERROR log records to WARNING records if a particular set ofcriteria are met.
Filters can be installed on loggers or on handlers; multiple filterscan be used in a chain to perform multiple filtering actions.
Formatters¶
Startupizer 2 3 3 – Advanced Login Handler Portal
Ultimately, a log record needs to be rendered as text. Formattersdescribe the exact format of that text. A formatter usually consistsof a Python formatting string containingLogRecord attributes; however,you can also write custom formatters to implement specific formatting behavior.