Vncviewer 5 1 0
If you don't have permission to install VNC® Viewer on desktop platforms, choose the standalone option. How do I control a remote computer? If you have a keyboard and mouse in front of you, use them as you would normally. If you're on a mobile device, then your touchscreen acts as a mouse trackpad, with gestures mapped to mouse buttons. If you need a version working in Windows 95/98/ME, Windows NT 4.0, or in Unix-like systems (including Linux), download TightVNC 1.3.10. Verify the Files. All executable files and packages (.EXE files) are digitally signed by GlavSoft LLC. Make sure to check the digital signatures.
VNC Viewer 5.1.0 + keygen crack patch. January 12, 2020. Copy Download Link (paste this to your browser) Comments. Name. Email. Website. You may use these. BVNC Pro - Secure VNC Viewer v5.0.1 b115019 Paid Requirements: 4.0+ Overview: bVNC is a secure, open source VNC client. Thank you for supporting my work and GPL open-source software by donating! Please also rate my application, and tell everyone about it! If you need an RDP application, please search. Download Vnc Viewer 5.1.0 - real advice.
Contents
- Configuring un-encrypted VNC
- Test each VNC user
- VNC-Server for an already logged in GUI console session - 2 options
VNC is used to display an X windows session running on another computer. Unlike a remote X connection, the xserver is running on the remote computer, not on your local workstation. Your workstation ( Linux or Windows ) is only displaying a copy of the display ( real or virtual ) that is running on the remote machine.
There are several ways to configure the vnc server. This HOWTO shows you how to configure VNC using the 'vncserver' service as supplied by CentOS.
1. Installing the required packages
The server package is called 'vnc-server'. Run the command: rpm -q vnc-server
The result will be either package vnc-server is not installed or something like vnc-server-4.0-11.el4.
If the server is not installed, install it with the command: yum install vnc-server
The client program is 'vnc'. You can use the command: yum install vnc to install the client if: rpm -q vnc shows that it is not already installed.
Make sure to install a window manager in order to get a full-featured GUI desktop. You can use the command yum groupinstall 'GNOME Desktop Environment' to install the Gnome Desktop and requirements, for example. Other popular desktop environments are 'KDE' and 'XFCE-4.4'. XFCE is more light-weight than Gnome or KDE and available from the 'extras' repository.
If you are a minimalist, or simply testing, however, it is sufficient to have yum install a simple XTERM client: yum install xterm
If you are running CentOS 6, the command is yum groupinstall Desktop
If you are running CentOS 5, yum groupinstall 'GNOME Desktop Environment' may complain about a missing libgaim.so.0. This is a known bug. Please see CentOS-5 FAQ for details.
If you are running CentOS 6, the server is: tigervnc-server not: vnc-server
2. Configuring un-encrypted VNC
We will be setting up VNC for 3 users. These will be 'larry', 'moe', and 'curly'
You will perform the following steps to configure your VNC server:
- Create the VNC users accounts.
- Edit the server configuration.
- Set your users' VNC passwords.
- Confirm that the vncserver will start and stop cleanly.
- Create and customize xstartup scripts.
- Amend the iptables.
- Start the VNC service.
- Test each VNC user.
- Additional optional enhancements
2.1. Create the VNC user accounts
As root:
2.2. Edit the server configuration
Edit /etc/sysconfig/vncservers, and add the following to the end of the file.
Larry will have a 640 by 480 screen, as will Moe. Curly will have an 800 by 600 screen.
Note: This step is NOT out of sequence, but is placed here so that the next following step will fall adjacent to the step in which failure to perform it, will permit immediate fault diagnosis.
2.3. Set your users' VNC passwords
Switch user into the account for each user, and as noted below, run: vncpasswd This will create the ~/.vnc directory for that userid:
2.4. Confirm that the vncserver will start and stop cleanly
We will create the xstartup scripts by starting and stopping the vncserver as root. We also enable the vncserver service to be automatically started.
Note: if you omitted the preceding step of logging in as each configured user, and creating their ~/.vnc/ subdirectory, this test will fail.
2.5. Create xstartup scripts ( You may omit this step for CentOS 6 )
Login to each user and edit the xstartup script. To use Larry as an example, first login as larry
Edit ~/.vnc/xstartup for each user. The original should appear as follows:
Add the line indicated below to assure that an xterm is always present, and uncomment the two lines as directed if you wish to run the user's normal desktop window manager in the VNC. Note that in the likely reduced resolution and color depth of a VNC window the full desktop will be rather cramped and a look bit odd. If you do not uncomment the two lines you will get a gray speckled background to the VNC window.
2.6. Amend the iptables
The iptables rules in /etc/sysconfig/ need to be amended to open the VNC ports; as needed, if a local ipv6 setup is being used, those need to be amended as well:
... and then restart the iptables:
2.7. Start the VNC server
Start the vncserver as root.
2.8. Test each VNC user
2.8.1. Testing with a java enabled browser
Let us assume that mymachine has an IP address of 192.168.0.10. The URL to connect to each of the users will be:
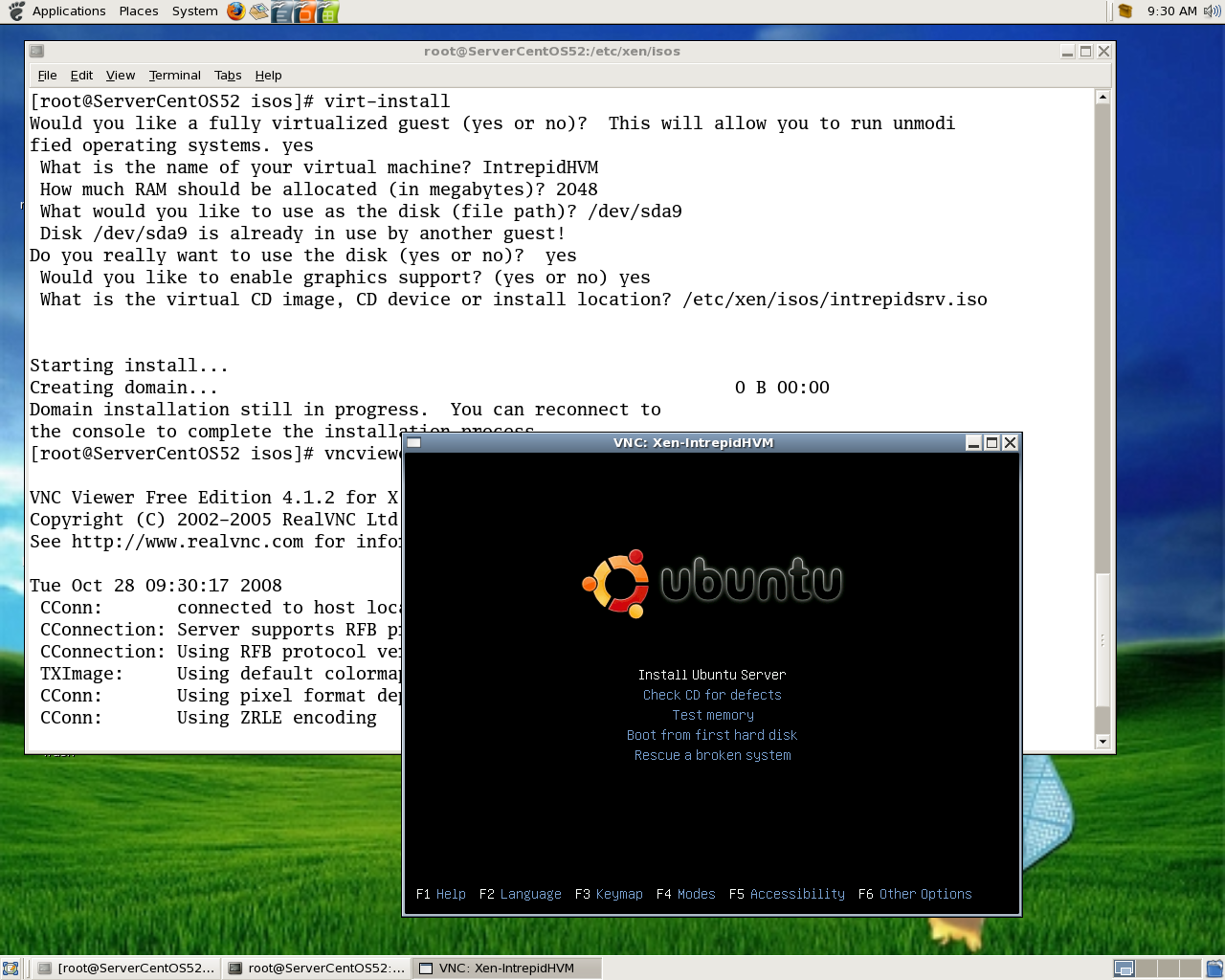
Connect to http://192.168.0.10:5801. A java applet window will pop-up showing a connection to your machine at port 1. Click the [ok] button. Enter larry's VNC password, and a 640x480 window should open using the default window manager selected for larry . The above ports 5801, 5802 and 5803 must be open in the firewall {iptables) for the source IP addresses or subnets of a given client.
2.8.2. Testing with a vnc client
To test larry using vncviewer, vncviewer 192.168.0.10:1 An authentication box will pop up, and you may enter Larry's VNC password. Once authenticated, a 640x480 window should open using Larry's default window manager. The vncviewer client will connect to port 590X where X is an offset of 1,2,3 for Larry, Moe, and Curly respectively, so these ports must be open in the firewall for the IP addresses or subnets of the clients.
If your local account userid is not, say, larry, you may 'switch user' for purposes of vncviewer thus: {{{ export USER=larry ; vncviewer 192.168.0.10:1 }}} which has the effect of passing the username larry to the vncviewer program.
2.8.3. Starting vncserver at boot
To start vncserver at boot, enter the command: {{{/sbin/chkconfig vncserver on }}}
For basic VNC configuration the procedure is now complete. The following sections are optional refinements to enhance security and functionality.
3. VNC encrypted through an ssh tunnel
You will be connecting through an ssh tunnel. You will need to be able to ssh to a user on the machine. For this example, the user on the vncserver machine is: larry That account username needs to exist on the target machine, and either password, or keyed ssh access needs to be functional. the vncserver will also prompt for the vncpassword. The Linux and VNC system usernames and passwords are not required to be identical and are 'not' automatically synchronized. That is, remote users able and baker may each have differing credentials to set up the ssh tunnel to the remote VNC server, but if each uses the larry account, they will use the same VNC password.
Edit /etc/sysconfig/vncservers and add the option -localhost
/sbin/service vncserver restart
- Go to another machine with vncserver and test the VNC.
vncviewer -via larry@192.168.0.10 localhost:1
vncviewer -via moe@192.168.0.10 localhost:2
vncviewer -via curly@192.168.0.10 localhost:3
By default, many vncviewers will disable compression options for what it thinks is a 'local' connection. Make sure to check with the vncviewer man page to enable/force compression. If not, performance may be very poor!
4. Recovery from a logout ( Not implemented for CentOS 6 )
If you logout of your desktop manager, it is gone!
- We added a line to xstartup to give us an xterm where we can restart our window manager.
For gnome, enter gnome-session.
For kde, enter startkde.
5. Remote login with vnc-ltsp-config
To allow remote login access via a vnc-client to the Centos system, the RPM packages named vnc-ltsp-config and xinetd can be installed. When a vnc-client connects to one of the configured ports, the user will be given a login screen. The sessions will *not* be persistent. When a user logs out, the session is gone.
The rpm package vnc-ltsp-config is easily installed via the EPEL repository noted in Available Repositories
Note: There are no major dependencies for the package so the vnc-ltsp-config*.rpm could easily be downloaded and installed without the need for enabling the EPEL repository.
Install, as root via:
Next, as root edit the file '/etc/gdm/custom.conf'.
- To the next blank line below the '[security]' section add 'DisallowTCP=false'
- To the next blank line below the '[xdmcp]' section add 'Enable=true'
- Make sure you are in a position to either run 'gdm-restart' for default Gnome installs or just reboot the CentOS box.
This will add the ability to get the following default vnc-client based session connections:
resolution | color-depth | port |
1024x768 | 16 | 5900/tcp |
800x600 | 16 | 5901/tcp |
640x480 | 16 | 5902/tcp |
1024x768 | 8 | 5903/tcp |
800x600 | 8 | 5904/tcp |
640x480 | 8 | 5905/tcp |
If you don't like the above defaults, just modify /etc/xinetd.d/vncts as required.
A major advantage of using the vnc-ltsp-config setup is the reduction of system resource utilization compared to the standard 'per-user setup'. No user processes will be started or memory consumed until a user actually logs into the system. Also, no pre-thought for user setup is needed (eg skip all of the manual individual user setup for vnc-server). The downside to the vnc-ltsp-config setup is that *any* user with the ability to login will likely have the ability to log into the system via a vnc-client with full gui unless steps are taken to limit that type of access. Also, there is no session persistance! Once the vnc-client closes, the vnc-ltsp-config session will terminate (by default) and all running processes will be killed.
This option can be combined with ssh tunnelling using a slightly modified version of the 'vncviewer -via' command noted above:
For the default vnc-ltsp-config install, the 'vncSinglePortNumber' is the last digit only of the port number. Port 5900 (1024x768 16bit) would just be '0', for example.
Note: you will need to be aware of possible interaction issues if you enable either selinux or iptables. If you are not running a display manager (runlevel 3 for example), you will need to start one or you will only get a black screen when you connect.
6. VNC-Server for an already logged in GUI console session - 2 options
Often you will need remote access to an already logged in GUI session on a 'real' console. Or you will need to help another user remotely with an GUI or visual issue. You will need either 'vnc-server' or 'x11vnc'. The vnc-server option will be a module added to X11 for 'allways on' vnc support, while x11vnc will allow for adhoc vnc support.
vnc-server install will require no third party repos or source building.
x11vnc is a way to view remotely and interact with real X displays (i.e. a display corresponding to a physical monitor, keyboard, and mouse) with any VNC viewer. In this way it plays the role for Unix/X11 that WinVNC plays for Windows.
6.1. x11vnc adhoc option
Karl Runge has generously provide a exceptional amount of information at http://www.karlrunge.com/x11vnc/ for x11vnc. There is info on securing the connection and also an 'Enhanced TightVNC Viewer (ssvnc)'. To make it easy, follow these steps:
1. Download the latest rpm install from http://dag.wieers.com/rpm/packages/x11vnc/ to the host you want the vnc-client to connect to:
2. Install, as root, via the yum or rpm programs on the host you want the vnc-client to connect to:
Vnc Viewer 5.1.0
3. Start the x11vnc process on the host you want the vnc-client to connect to. Please take a long look at the possible options from the x11vnc website. A very simple/insecure example for a trusted network setup (local network or VPN) is to have the user with the GUI console issue the command:
Then connect (without password) via a vnc-client to the IP/hostname and port noted by the x11vnc command. By default, x11vnc will allow connections from all interfaces. Host based firewall settings may need to be modified.
You can combine this with ssh tunneling:
Note that the -C flag is for compression, so may not be required
6.2. vnc-server X11 'always on' option
1. On the the system you want to run vnc-server, install vnc-server as noted above.
2. Edit /etc/X11/xorg.conf, as root, and add/create a 'Module' Section and add 'Load 'vnc':
3. For standard vnc authentication, edit /etc/X11/xorg.conf, as root, and add to the 'Screen' Section:
4. As root, run 'vncpasswd' to create the password noted above.
5. Restart X11 (<Ctrl>+<Alt>+<BS> will work if on the console already)
6. You should be able to connect with a vncviewer client as normal.
7. To trouble shoot, check for errors in the /var/log/Xorg.0.log or verify that iptables or selinux is not interfering with remote connections. Additional information is at http://www.realvnc.com/products/free/4.1/x0.html
This Fedora Tutorial has been found useful by some users.
|
|
|
|
sponsored links
MSI
|
|
Setup select the best version for your OS, installer contain different compiled versions of the exe.
Addons installer contain the (mirror driver-schook,encryption plugins-w8hook-w8keys)
Binary zips (changed files)
|
Vnc Viewer 5.1.1
|
|
|
Remark bins: Never extract the exe direct (via iexplorer) from the zip.
If you extract them direct, uac mark the files as unsecure... and winvnc server doesn't work proper.
First save as zip then open via explorer...
Viewer Translations ( rename dll to vnclang.dll)
|
Mirror Driver
|
SourceCode
|
Changes
**********************************************
* Ultr@VNC - Latest modifications - History
**V1.1.9.6 Dec 2013
*auto alpha blending based on OS*zrle deadlock fix
*tight encoding fixed
*show screenbuildup on first run
*server fix bug that crashed iexplorer 8
**V1.1.9.4 Okt 2013
*viewer mod for vmware ( wrong colors)
*update lijpeg-turbo to 1.3.0
**V1.1.9.3 Aug 2013
-Missing screen refresh ( when driver selected but not used)
-Factory reset ( when temp was not writable)
**V1.1.9.2 Aug 2013
-Mirror driver and begative screen coordinates (left secondary desktop)
**V1.1.9.0 May 2013
-fixed change ip detection, sometimes server was disconnected after a few seconds by a false positive
-new installer xp64 wasn’t supported
**V1.1.8.9 April 2013
-Viewer timeout option grayscreen fix
-server leaks fixed
**V1.1.8.8 March 2013
-server crash
-server grayscreen on startup loop fixed
**V1.1.8.7 March 2013
-filetransfer bug fix (x64)
**V1.1.8.6 March 2013
-autoreconnect and auth fail fix
-viewer with option window open fails to close
-viewer messagebox sometimes hidden behind window
**V1.1.8.5 March 2013
deadlock softcursor fixed (viewer)
**V1.1.8.4 March 2013
server
-u2 encode on 16 color display crash
viewer
-fullscreen bar center
-recoonect set by default
**V1.1.8.3 March 2013
-Fix server /NULL crash
-Fix radio button u2 viewer
**V1.1.8.2 March 2013
-fix lock after gray screen
**v1.1.8.2 (March 2013)
-disconnect after gray screen
**v1.1.8 (Nov 2012)
-addad support windows 8
( new capture engine)
-several bug fixes
-better multi monitor support
-new vncpasswd + encryption.
Instead of using the password as part of the encryption, we now check the password insite the encryption by the server. This allow the server to balcklist servers
after x fault password.
WARNING: If using encryption plugin + vncpassword you better upgrade. No protection against Brute force password hacking.
**v1.0.9.6.2 (Feb 2012)
-removed beeps
-Capture alpha-Blending default value.
-Viewer crash fixed
-Grayscale fixed
-msi installers
server
*crash chat x64
*AuthRequired=0, passwd=NULL: Warning message block service
*About x64 say win32
*viewer 1082 and server 1096 with localcursor ( no connect, 100% cpu)
*serversite scaling and multiple viewers, framebuffer size get overwritten
(Scale is now lock when multiple viewers are connected to avoid a
framebuffer change, first connected viewer set scale. Site effect is that
the viewer report the unused, incorrect scale, but at least it doesn't crash anymore)
*-connect ip, passed to winvnc running as service is not remembered for
autoreconnect.
*-stopreconnect
stop the autoreconnect function of the server.
*server mouse moves jump on viewer when screen is idle.
*old plugin zrle crash
viewer
*plugin (SecureVNCPlugin) used by viewer
server without plugin
give incorrect viewer message. And doesn't ask to reject the connection.
*monitor value is saved, but vncviewer read it as bool (true/false)
Only 0/1 are correct imported
*old plugins fail when zrle encoding is used
*old plugins give incorrect info in statusbox
*-autoreconnect timeout, -reconnectcounter number
(available from gui and commandline)
-autoreconnect timeout was incorrect, updated
*old plugin detection
*Messagebox was sometimes displayed on invisable desktop
*auth dll error messages for missing dll's incorrect
*mslogon and no groups, didn't checked admin account for access
*lock /logout screen on exit viewer option blocked shutdown server.
javaviewer
*mslogon fixed
added special build: only one port for javaviewer (rfb port is used for java download and rfb data)
License
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE (GPL)
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
http://www.gnu.org/licenses